개요
- law of sines, sine law, sine formula, or sine rule
- 사인 법칙, 정현법칙, 정현정리
- 삼각형에서 내각 사인값과 대변 길이의 관계
<math>{a \over {\sin A}} = {b \over {\sin B}} = {c \over {\sin C}} = 2R</math>
- R=외접원의 반지름
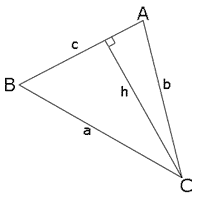
기본 증명
- <math>\sin A = \frac{h}{b}</math>, <math>\sin B = \frac{h}{a}.</math>
- <math>h = b\,\sin A = a\,\sin B</math>
- <math>\frac{a}{\sin A} = \frac{b}{\sin B}</math>
B와 C도 마찬가지.
2R 증명
90° 미만
△ABC의 외접원과, 그 중심을 지나는 내접△ BCD를 작도

- <math>\angle \rm A =\angle D</math> (원주각의 정리)
- <math>\overline{BD} = 2R</math>, <math>\angle {\rm BCD} = {\pi \over 2}</math>
- <math>\sin D = {a \over 2R}</math>
- <math>\qquad\sin D = \sin A</math>
- <math>{a \over \sin A} = 2R</math>
<math>\angle B</math>, <math>\angle C</math>도 마찬가지.
90° 초과

- <math>\angle \rm D = \pi - \angle A</math>
- <math>\sin D = \sin A</math>
- <math>{\sin A} = {\sin D} = {a \over 2R}</math>
- <math>{a \over \sin A} = 2R</math>
<math>\angle B</math>, <math>\angle C</math>도 마찬가지.